404 Brain Not Found
[자료구조] Deque 본문
분류:
- 선형 자료구조
- 양방향 입출력 구조
특징:
- 양쪽 끝에서 삽입과 삭제가 모두 가능한 자료구조
- Queue와 Stack의 특성을 모두 가짐
- 네 가지 기본 연산 제공: 전단 삽입/삭제, 후단 삽입/삭제
- 양쪽에서 데이터 접근이 가능하므로 더 유연한 데이터 관리 가능
- 일반적으로 동적 할당 배열이나 이중 연결 리스트로 구현
- 원소의 개수가 n개일 때, 양 끝 원소의 삽입/삭제는 O(1) 시간 복잡도를 가짐
사용처:
- 앞뒤로 제거와 삽입이 자주 일어나는 자료구조가 필요한 경우
- 웹 브라우저의 방문 기록 (앞으로 가기/뒤로 가기)
- 문자열 편집기에서 undo/redo 기능 구현
- 작업 스케줄링 (우선순위에 따라 앞뒤로 작업 추가/제거)
- 회문(palindrome) 검사
- 슬라이딩 윈도우 관련 문제 해결
- 큐와 스택을 동시에 활용해야 하는 알고리즘
#pragma once
template<typename T>
class Deque
{
private:
int _size; // deque 사이즈
int _capacity; // deque 용량
T* _data; // data 버퍼
int _front; // front Index
int _end; // end Index
public:
// 생성자
Deque() : _size(0), _capacity(0), _data(nullptr), _front(0), _end(0) {}
// 소멸자
~Deque()
{
if (_data)
delete[] _data;
}
public:
void Reserve(int newCapacity)
{
T* newData = new T[newCapacity]; // 새로운 버퍼를 할당받는다.
if (_data)
{
// end 인덱스가 front 인덱스보다 작다면 버퍼를 넘어간 케이스
// [][E][][F][]
if (_end <= _front)
{
// front 인덱스부터 배열의 끝부분까지 복사
::memcpy(newData, &_data[_front], (_capacity - _front) * sizeof(T));
// 0번째 인덱스부터 end 인덱스 전 까지 복사
::memcpy(newData + (_capacity - _front), &_data[0], _end * sizeof(T));
// Front Index와 End Index 재지정
// 새로운 메모리로 이동하였으므로, _front는 0번 인덱스가 되고, _end는 _size가 된다.
_front = 0;
_end = _size;
}
// 그렇지 않을 경우 직관적인 Case
// [][F][][][E]
else
{
::memcpy(newData, &_data[_front], (_end - _front) * sizeof(T));
// Front Index와 End Index 재지정
// 새로운 메모리로 이동하였으므로, _front는 0번 인덱스가 되고, _end는 _end - _front가 된다.
_front = 0;
_end = _end - _front;
}
}
_capacity = newCapacity; // capacity 갱신
if (_data) // 이전 버퍼 메모리 할당 해제
delete[] _data;
_data = newData; // 새로 할당받은 버퍼를 가리키도록 갱신
}
// push_front: frount Index를 한칸 전진하고 데이터를 넣는다
void PushFront(const T& data)
{
int nextSize = _size + 1;
if (_capacity < nextSize)
{
Reserve(nextSize * 1.5);
}
_front = _front - 1;
if (_front < 0)
_front += _capacity;
_data[_front] = data;
_size = nextSize;
}
// push_back: 데이터를 넣고 end Index를 한칸 후진한다.
void PushBack(const T& data)
{
int nextSize = _size + 1;
if (_capacity < nextSize)
{
Reserve(nextSize * 1.5);
}
_data[_end] = data;
_end = (_end + 1) % _capacity;
_size = nextSize;
}
void PopFront()
{
int nextSize = _size - 1;
if (nextSize < 0)
{
throw std::runtime_error("Deque is Empty");
}
_front = (_front + 1) % _capacity;
_size = nextSize;
}
void PopBack()
{
int nextSize = _size - 1;
if (nextSize < 0)
{
throw std::runtime_error("Deque is Empty");
}
_end = _end - 1;
if (_end < 0)
_end += _capacity;
_size = nextSize;
}
const T& Front()
{
if (Empty())
{
// data가 없는데 Top을 했다는 것은, Error
throw std::runtime_error("Deque is Empty");
}
return _data[_front];
}
const T& Back()
{
if (Empty())
{
// data가 없는데 Top을 했다는 것은, Error
throw std::runtime_error("Deque is Empty");
}
int index = _end - 1;
if (index < 0)
{
index = _end - 1 + _capacity;
}
return _data[index];
}
bool Empty()
{
return _size == 0;
}
};#include "pch.h"
#include <deque>
#include "Deque.h"
int main()
{
std::deque<int> dqq;
dqq.push_back(1);
dqq.push_back(2);
dqq.push_back(3);
dqq.push_back(4);
dqq.push_back(5);
dqq.push_front(6);
dqq.push_front(7);
dqq.push_front(8);
dqq.push_front(9);
dqq.push_back(10);
while (!dqq.empty())
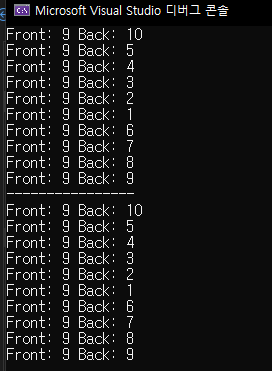
{
std::cout << "Front: " << dqq.front() << " Back: " << dqq.back() << std::endl;
dqq.pop_back();
}
std::cout << "----------------" << std::endl;
Deque<int> dq;
dq.PushBack(1);
dq.PushBack(2);
dq.PushBack(3);
dq.PushBack(4);
dq.PushBack(5);
dq.PushFront(6);
dq.PushFront(7);
dq.PushFront(8);
dq.PushFront(9);
dq.PushBack(10);
while (!dq.Empty())
{
std::cout << "Front: " << dq.Front() << " Back: " << dq.Back() << std::endl;
dq.PopBack();
}
return 0;
}실행 결과
구현 중요 포인트
deque를 구현하기 위해서는 queue 자료구조와 같이 frontIndex와 endIndex를 두어서 구현을 했습니다.
아래와 같이 메모리상에 배열이 위치하고 있다고 가정하겠습니다.
(queue 자료구조를 구현할 때처럼 Ring 버퍼로 구현을 합니다.)
[f/e][][][][]
f: frontIndex
e: endIndex
맨 처음에는 0번째 인덱스에서 시작합니다.
이때 psuh_front() 함수를 호출했다고 가정하겠습니다.
(front_push는 deque의 맨 앞에서부터 데이터를 삽입하는 것입니다.)
psuh_front의 로직은 front 인덱스를 한 칸 뒤로 후진하고, 데이터를 삽입합니다.
1. frontIndex를 전진합니다.
[e][][][][f]
2.frontIndex에 데이터를 삽입합니다.
[e][][][f(d)]
이제 push_back() 함수를 호출했다고 가정하겠습니다.
(front_back는 deque의 맨 뒤에서부터 데이터를 삽입하는 것입니다.)
1. endIndex에 데이터를 삽입합니다.
[e][][][][f]
2.endIndex를 후진합니다.
[(d)][e][][f(d)]
해당 방식을 구현하면 이렇습니다.

만약에 [(d)][(d)][(d)][e/f(d)] 이런 상황일 경우 (데이터가 가득 찼을 경우)
RingBuffer의 특성을 고려해서 새로운 메모리를 할당받고, 새로운 메모리에 이전 메모리 데이터 복사를 해줍니다.

'자료구조 > 선형자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] ArrayList (0) | 2024.09.16 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] Queue (7) | 2024.09.16 |
| [자료구조] Stack (2) | 2024.09.16 |